TOKYO, JAPAN — Dentsu Inc. (Headquarters: Minato-ku, Tokyo; President & CEO: Norihiro Kuretani), today announced that it has conducted its fifth Consumer Survey on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs; hereinafter, “the survey”), which was carried out by Dentsu Team SDGs, a Dentsu Group-wide working group tasked with promoting projects related to the SDGs.1 The survey gathered data across Japan from 1,400 male and female respondents between the ages of 15 and 79.
The survey compares SDG awareness rates, information channels, and evaluations of companies working to achieve SDGs with past survey results, and in particular, newly analyses generational characteristics among those highly motivated to commit to the SDGs.
The survey’s key findings are summarized below.
1. The SDG awareness rate is 86.0%, an increase of more than 30 percentage points over the fourth survey,2 conducted in January 2021, and approximately six times higher than the first survey, carried out in February 2018.
2. Compared with the fourth survey, respondents indicating they are aware, and understand the details, of the SDGs show an approximately 1.5-fold increase to 34.2%. For the first time, more than 50.0% of teens respond likewise.
3. Among those aware of the SDGs, 36.9% are highly motivated to commit to the SDGs. To appeal to this group, it is necessary to provide information demonstrating specific facts and connections to the SDGs to gain the group’s understanding and empathy. It is also clear that topicality in the media and third-party opinions are important.
4. Among those highly motivated to contribute to the SDGs, Generation Z3 is very concerned about gender inequality, and has every intention of participating in SDG-related events, as well as consuming related products and services. Impacted by influencers and advertising, they share information through social media and conversation with family and friends.
5. This indicates that consumers not only have a good impression of companies that are proactively working to help attain the SDGs, but they also are willing to use those companies’ products and services.
Notes:
1. The goals were adopted by the United Nations Sustainable Development Summit in September 2015. The 193 member countries of the UN General Assembly set the goals, hoping to achieve them between 2016 and 2030. All UN member states agreed on the 17 goals and 169 specific targets, with the objective of solving major global issues and building sustainable societies.
2. The fourth Consumer Survey on Sustainable Development Goals was conducted between January 22 and 25, 2021.
3. Generation Z (Gen Z) refers to young people born between the mid-1990s and early 2000s. Critical in terms of becoming key drivers of consumption, members of Gen Z are attracting attention as influencers of values and trends throughout the world. (In this survey, Gen Z is represented in the totals for male and female aged 15-24 years).
Survey Findings
1. The SDG awareness rate is 86.0%, an increase of more than 30 percentage points over the fourth survey conducted in January 2021, and approximately six times higher than that of the first survey, carried out in February 2018.
● Awareness of the term SDGs is 86.0%, an increase of more than 30 points from 54.2% in the fourth survey. In the first survey, the awareness rate is 14.8%, mainly representing business people, thus it can be said that awareness has almost completely permeated the general population in four years. This is due to advances in promoting understanding in academic settings, facilitating understanding among the general population through mass media coverage, and an increasing number of corporate and government initiatives that have expanded opportunities to learn about the SDGs. [Graph 1]
● By gender and age, SDG awareness is highest among men in their 60s (94.9%), teen males (94.6%), and men in their 30s (91.8%). By occupation, awareness is highest among office workers (94.5%), civil servants (92.4%), and students (92.0%). The largest increase in awareness compared with the fourth survey is among women in their 70s (+50.5 percentage points), women in their 60s (+45.3 percentage points), and men in their 60s (+44.4 percentage points). The results demonstrate that awareness has spread among not only business people and students, but also the general population. [Graphs 2 and 3]
Graph 1. Awareness of SDGs

Graph 2. Awareness of SDGs (by Gender and Age)

Graph 3. Awareness of SDGs (by Occupation)

2. Compared with the fourth survey, respondents indicating they are aware of the SDGs and their details have increased an approximately 1.5-fold, expanding to 34.2%. For the first time, more than 50.0% of teens indicate likewise.
● Compared with the fourth survey, respondents indicating they are aware of the SDGs and understand the details show a 1.5-fold increase, expanding to 34.2%, or approximately 10 times higher than in the first survey (February 2018). By generation, teens (52.5%) are in the majority for the first time. [Graph 4]
● In terms of pathways to awareness, as in the fourth survey, television programs (65.4%), online information4 (38.6%), and newspapers (25.5%) rank highest, with television programs 18.1 percentage points higher. This is thought to be due to a substantial increase5 in the number of SDG-themed television programs. [Graph 5]
4. Such as news websites and curated media.
5. There were 493 terrestrial broadcasts of television programs (segments) focused on the SDGs in 2020 and 2,836 in 2021 in the greater Tokyo and Osaka urban-areas.
Graph 4. Understand SDG Details (by Age)

Graph 5. Pathways to Awareness

3. Among those aware of the SDGs, 36.9% are highly motivated to commit to the SDGs. To appeal to this group, it is necessary to provide information demonstrating specific facts and connections to the SDGs to gain understanding and empathy. It is also clear that topicality in the media and third-party opinions are important.
● When asking those aware of the SDGs what their impression about them is, the top response is, “I believe they are important” (49.9%). Meanwhile, 36.9% of respondents (multiple answers) say they are motivated to help attain the SDGs, their responses being, “I want to do something” (26.3%), “I want to know more” (17.5%), and “I want to tell people about them” (5.2%). At the same time, 39.3% of respondents only understand and empathize. [Graph 6]
● By gender, 41.1% of men and 58.9% of women are motivated to help attain the SDGs. By age, middle-aged respondents (in their 60s: 19.1%; 70s: 18.7%; 40s: 17.9%) rank highest. By occupation, those ranking highest are full-time housewives/househusbands at 20.1%, company employees (administrative) at 12.3%, and part-time/temp workers at 11.5%. [Graph 7, 8 and 9]
● By comparing respondents highly motivated to commit to the SDGs with those who only understand and empathize with the goals, and comparing the two groups of respondents in terms of the impetus for having an interest in SDG-related activities, products, and services, as well as having a sense of crisis concerning food loss and environmental, social, and human rights issues, notably high are values such as “always want to contribute to society and the global environment in line with personal ideals” and “topicality in the mainstream and social media.” [Graph 10]
● By the same comparison as above, and in terms of the selection criterion for SDG-related products and services, the largest number of responses are, “clearly explains relationship to SDGs,” “receiving coverage in the media,” and “solid research and technology.” [Graph 11]
Graph 6. Impression of the SDGs

Graph 7. Highly Motivated to Commit to the SDGs (by Gender)

Graph 8. Highly Motivated to Commit to the SDGs (Composition Ratio by Age)

Graph 9. Highly Motivated to Commit to the SDGs (Composition Ratio by Occupation)

Graph 10. Impetus for Having an Interest in SDG-related Activities, Products, Services (In descending of number of differences)

Graph 11. Selection Criterion for SDG-related Products, Services (In descending of number of differences)

4. Among those highly motivated to take action to help attain the SDGs, Generation Z is very concerned about gender equality, while having every intention of participating in SDG-related events and using related products and services. Affected by influencers and advertising, they share information through social media and conversation with family and friends.
● Among those highly motivated to commit to the SDGs, Gen Z is the group with characteristics worth watching. SDG-related information obtained through “workplace duties and school lessons” (52.2%), “conversation with family, friends, and acquaintances” (24.6%), and “social media” (19.4%) rank highest. In terms of practices already being followed, “taking action and speaking out about gender inequality and discrimination” (32.3%), “consumption of plant-based foods” (18.1%), and civic activities (regional contributions, volunteering, NPO activities, etc.” (19.3%) are relatively high. [Graphs 12 and 13]
● Compared with the rest of those highly motivated to commit to the SDGs, another characteristic of Gen Z that stands out is that most say they “learned about the SDGs during class at school or while at work” (51.7%), leading to their interest in SDG-related products and services. [Graph 14]
● Another feature of Gen Z expectations is that the SDG-related products and services have “influencer coverage” (20.6%), “give them a feeling of pride and fulfillment” (18.7%), and “are advertised and popular” (19.8%). This shows that the best way to appeal to Gen Z is through influencers, advertising, social media, and their conversations with family and friends. [Graph 15]
Graph 12. Pathways to Awareness (In descending of number of differences)

Graph 13. SDG-related Activities (In descending of number of differences)

Graph 14. Impetus for Having an Interest in SDG-related Products, Services (In descending of number of differences)

Graph 15. Selection Criterion for SDG-related Products, Services (In descending of number of differences)

5. This indicates that consumers not only have a good impression of companies which are proactively working toward the SDGs, but also that they are more willing to use those companies’ products and services.
● Regarding companies proactively engaged in the SDGs, the responses that rank high include “the company’s image improved” (40.0%), “I want to support/like them” (35.2%), and “I trust the company” (26.6%). In addition to having a favorable impression of a company, nearly 20% of respondents indicate they “want to use that company’s products or services” (18.1%). [Graph 16]
● Among the respondents currently involved in SDG-related activities, 41.7% indicate they want to use the products or services of companies engaged in SDG-related activities. When considering the feedback from all the survey respondents, including those not currently involved in SDG-related activities, they account for more than double the 18.1% of all the survey respondents. This suggests that, were the details of the SDGs understood and disseminated, and the number of those involved in promoting SDG-related activities increased, people’s impression of the companies involved would improve. Moreover, those people’s intention to purchase and use such companies’ products and services would increase.[Graph 17]
● Further, among the respondents who are working, 33.6% are aware of their respective employer’s SDG-related initiatives, while 61.8% of them have a positive impression, expressed as, “I want to tell the world that the company is engaged in SDG-related activities” (19.1%) and “I have high hopes for the future of my company” (16.3%). Among men in their 30s, the highest-ranking responses include “I feel proud” (21.7%), “I want to continue working at my company” (21.1%) and “I find it rewarding to work for a company involved in SDG-related activities” (20.7%). [Graphs 18, 19 and 20]
Graph 16. Result of Image Created by Companies Working to Attain SDGs (In descending of number of answers)

Graph 17. Intention to Use Products, Services of Companies Engaged in Helping Attain the SDGs

Graph 18. Employees’ Awareness of SDG-Initiatives of Own Company
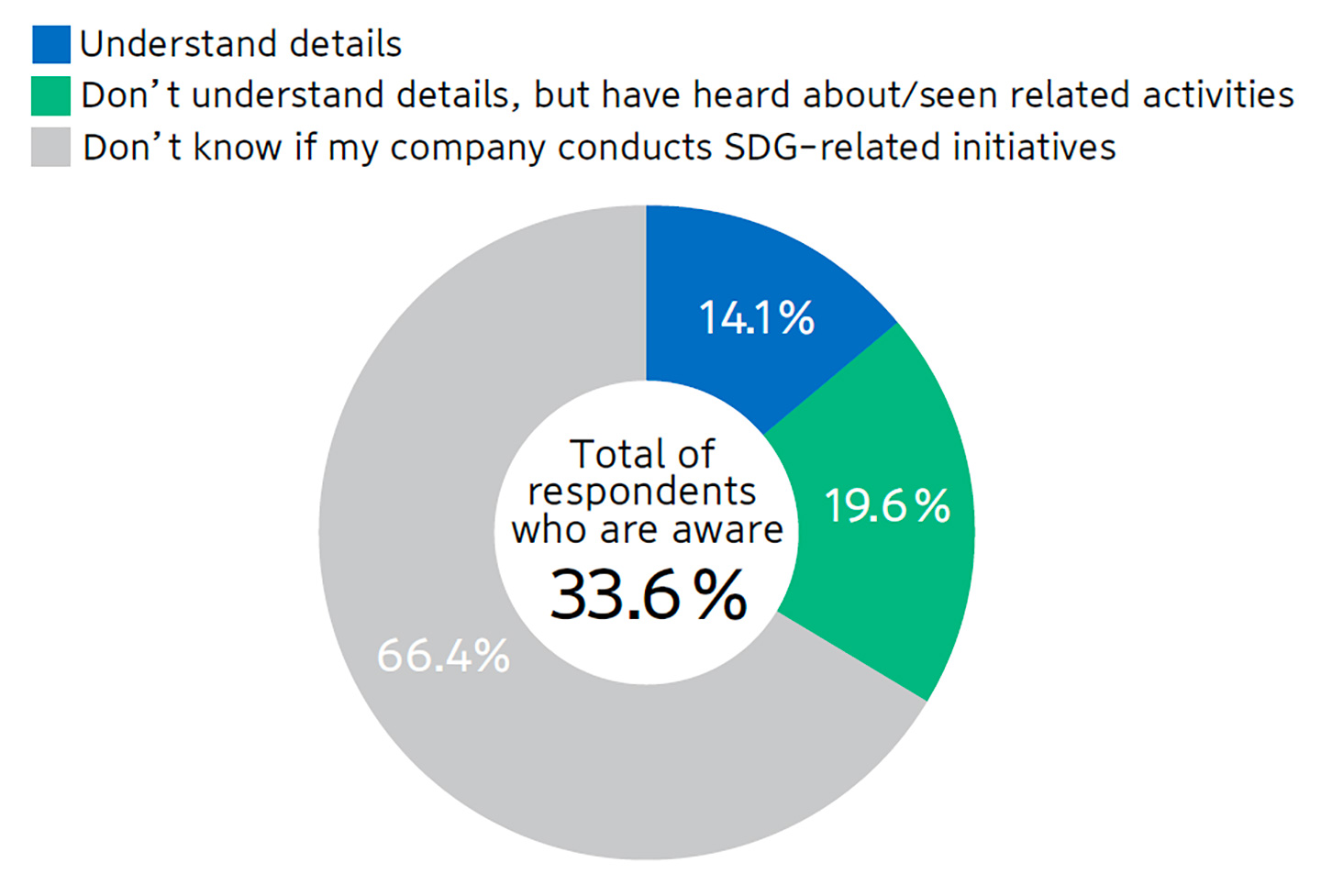
Graph 19. Impression of Own Company’s SDG Initiatives

Graph 20. Impression of Own Company’s SDG Initiatives (Breakdown)

Comment by Ms. Nanette Braun
Chief, Communications Campaigns Service
Strategic Communications Division
Department of Global Communications
United Nations
“We are deeply appreciative of Dentsu’s continued commitment to the Sustainable Development Agenda. This fifth consumer survey conducted by Dentsu provides once again important insights. The findings are highly encouraging, with a recognition rate of the SDGs now at 86%, an increase by 30 percentage points from last year, and an almost 6-fold leap from its first survey in 2018. This is significant because achieving the Sustainable Development Goals is everybody’s business. What’s more, people seem to be willing to make sustainability their business: as we can see from the survey results, not only has general awareness increased, but also the willingness to take action to advance the SDGs. Most encouragingly, we see that teenagers are highly motivated to engage on the issues addressed in the Sustainable Development Agenda, notably in particular on gender equality. The youth of GenZ will shape the future of our societies and their involvement represents a bright outlook indeed in the Decade of Action leading up to 2030, as we need to accelerate SDG action at all levels to deliver on their promise. Thanks to Dentsu’s survey, we know more about how to meaningfully respond to and nurture interest to broadly engage people on this critical agenda.”
Outline of Fifth Consumer Survey on Sustainable Development Goals
References
The first survey was released on April 4, 2018 (conducted on February 6 and 7, 2018)
https://www.dentsu.co.jp/news/release/2018/0404-009518.html (Japanese only)
The second survey was released on April 22, 2019 (conducted between February 7 and 18, 2019)
https://www.dentsu.co.jp/en/news/release/2019/0422-009821.html (English)
The third survey was released on April 27, 2020 (conducted on January 18 and 19, 2020)
https://www.dentsu.co.jp/en/news/release/2020/0427-010046.html (English)
The fourth survey was released on April 26, 2021 (conducted from January 22 to 25, 2021)
https://www.dentsu.co.jp/en/news/release/2021/0426-010368.html (English)